Top Family, Cosmetic and Implant Center In 537 Amherst St, Nashua, NH 03063
Tooth Infection Swollen Lymph Nodes and Treatment
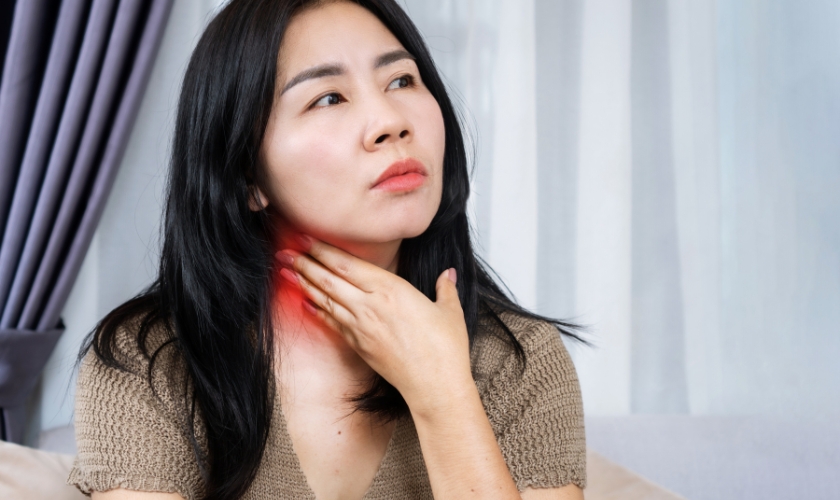
Picture this: you wake up one morning with a throbbing toothache. As the pain intensifies, you notice something else—swollen lymph nodes under your jaw on one side. What could be causing these symptoms? Could it be a tooth infection? The answer is yes! In this blog post, we will dive deep into the world of tooth infections and swollen lymph nodes, exploring their symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention tips.
Understaing Tooth Infections and Swollen Lymph Nodes
Bacteria can enter a tooth through a cavity, crack, or other dental problems, leading to tooth infections. The infection has the potential to spread to the tissues in the vicinity and even impact the lymph nodes.
Bad dental hygiene is one of the main causes of tooth infections. When we don’t regularly brush and floss, plaque accumulates on our teeth, giving dangerous bacteria a place to grow. These microorganisms have the ability to pierce the tooth’s enamel and induce an infection.
Did you know that approximately 10 to 20 percent of all lymph node enlargements are due to dental infections such as tooth abscesses? This alarming figure underscores the significant impact tooth infections can have on our health, particularly when it comes to swollen lymph nodes.
Swollen lymph nodes, also known as lymphadenopathy, refer to the enlargement of lymph nodes, which are small, bean-shaped structures found throughout the body. These nodes play a crucial role in the immune system, serving as filters that trap and destroy harmful substances like bacteria, viruses, and abnormal cells.
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection Swollen Lymph Nodes
- Toothache: A persistent pain, throbbing, or sensitivity in a specific tooth is a telltale sign.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Look for lumps under your jaw or neck, usually on the same side as the aching tooth. They might be tender or painful to the touch.
- Fever: A low-grade fever, especially if accompanied by chills, can indicate the body fighting infection.
- Facial swelling: In some cases, swelling might extend to your cheek or jaw, causing discomfort and asymmetry.
- Gum tenderness or redness: Inflammation around the infected tooth and its surrounding gums is a common symptom.
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing: Pain or discomfort while using your mouth can be another clue.
- Bad breath or a foul taste: The presence of bacteria and pus can lead to unpleasant odors.
- Spread of infection: The bacteria can travel to other parts of your body, causing serious health risks.
- Abscess formation: A painful collection of pus that requires immediate intervention.
- Bone damage: Untreated infections can erode the jawbone, potentially requiring complex treatments.
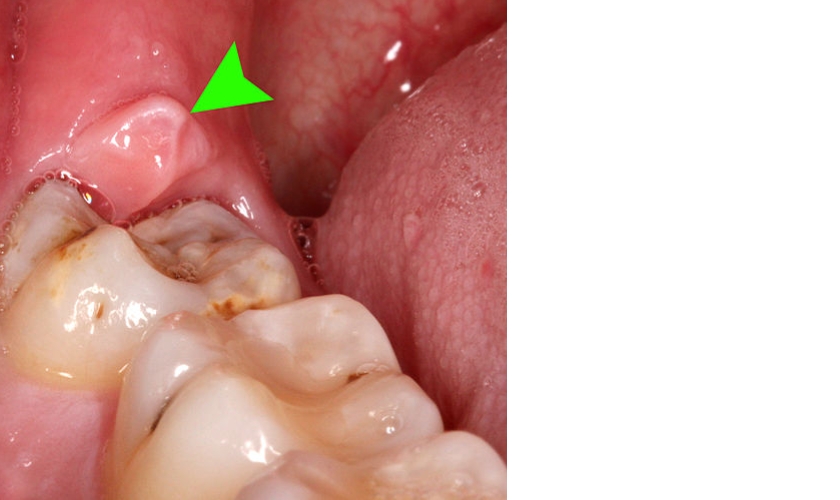
Causes of Tooth Infections Swollen Lymph Nodes
That nagging toothache isn’t just a nuisance; it could be a silent alarm for a brewing storm within your body. Swollen lymph nodes, those pea-sized lumps under your jaw or neck, often point to infection, and in up to 30% of cases, tooth infections are the culprit. Understanding the link between these two seemingly unrelated symptoms is crucial for safeguarding your oral and overall health.
- Cavities: Untreated cavities allow bacteria to infiltrate deeper tooth layers, leading to infection and inflammation.
- Gum Disease: This progressive disease weakens gum tissue, creating pockets where bacteria thrive and trigger infection.
- Cracked or Chipped Teeth: These openings serve as gateways for bacteria to invade the inner tooth, causing infection.
- Improper Dental Work: Faulty fillings, crowns, or root canals can harbor bacteria and lead to infection.
- Dental Injuries: Trauma to the tooth can damage nerves and blood vessels, increasing infection risk.
Your lymph nodes act as tiny filters, trapping bacteria and debris from nearby tissues. When a tooth infection flares up, the lymph nodes in your head and neck go on high alert, swelling as they work overtime to contain the invaders. This swelling is their way of signaling the immune system to fight the infection.
While tooth infections are a major cause, swollen lymph nodes can also stem from other head and neck issues, like:
- Ear infections
- Tonsillitis
- Sinusitis
Don’t Wait: Signs You Need Professional Help
Ignoring these signs can lead to severe complications, so be vigilant:
- Persistent toothache or sensitivity
- Tender, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or neck
- Fever, especially with chills
- Facial swelling
- Gum redness or pus
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Bad breath or foul taste
Treatment Options for Tooth Infections Swollen Lymph Nodes
Reducing inflammation and treating the underlying cause of the infection are the usual treatments for tooth infections and enlarged lymph nodes. It is imperative that you seek immediate dental care if you think you may have a tooth infection in order to avoid more complications.
Root canal therapy is a popular tooth infection treatment option. In order to stop reinfection, the infected pulp inside the tooth must be removed during this procedure and sealed. If a root canal is not an effective treatment for the infection, extraction may be required in certain cases.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to directly treat the infection or suggest over-the-counter pain relievers to reduce the swelling and discomfort associated with swollen lymph nodes. Rinses with warm saltwater can also aid in the healing and soothing of sore gums.
Prevention Tips for Avoiding Tooth Infections Swollen Lymph Nodes
It is essential to practice good oral hygiene in order to avoid swelling lymph nodes and tooth infections. The following advice will help you maintain the health of your gums and teeth:
- Brush twice a day: Ensure that you spend at least two minutes each time thoroughly cleaning your teeth with fluoride toothpaste. Remember to wash your tongue as well.
- Floss every day: Brushing may not be able to reach areas between your teeth where food particles and plaque are present. Regular flossing can help.
- Use mouthwash: To eliminate bacteria that cause oral infections, rinse your mouth with an antiseptic mouthwash after brushing and flossing.
- Schedule routine dental visits: Make an appointment for a dental examination at least twice a year to ensure thorough cleaning and early identification of any possible problems.
- Maintain a healthy diet and cut back on sugary drinks and foods, as they can aggravate tooth decay. Rather, choose nutrient-dense foods like dairy, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean meats.
- Steer clear of tobacco use: Gum disease, which can result in tooth infections, is increased by smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Protect Your Teeth During Sports Activities: When playing contact sports, wearing mouthguards lowers the risk of injury or trauma that could result in an infection.
Good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing frequently, are the first line of defense against dental infections. It is crucial to schedule routine cleanings and exams at Advanced Family Dentistry Nashua in order to identify any early indications of decay and treat them before they worsen.
Yes, any type of tooth infection, from a small cavity to a severe abscess, can trigger swollen lymph nodes.
With proper treatment, they usually subside within a few days to a week.
Seek immediate medical attention if the nodes are large, painful, red, or accompanied by fever or facial swelling.
Warm compresses and rest can offer comfort. However, they don’t treat the underlying infection.
Untreated, they can signal a serious underlying infection and lead to complications.
Antibiotics treat bacterial infections, and if the swollen nodes are due to a tooth infection,